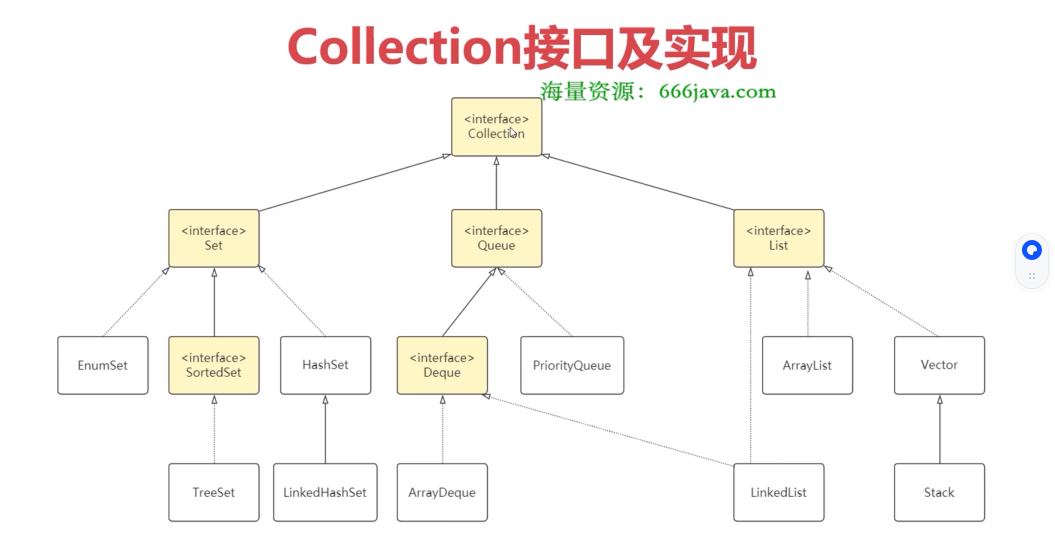
Java 集合
常见集合:List、Set、Map
Collections实现集合排序
字节/字符流:InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer
集合
概念:
Java中的一个工具类,用于存储数量不等的对象。
常用集合:
List:有序,可重复集合,有顺序索引
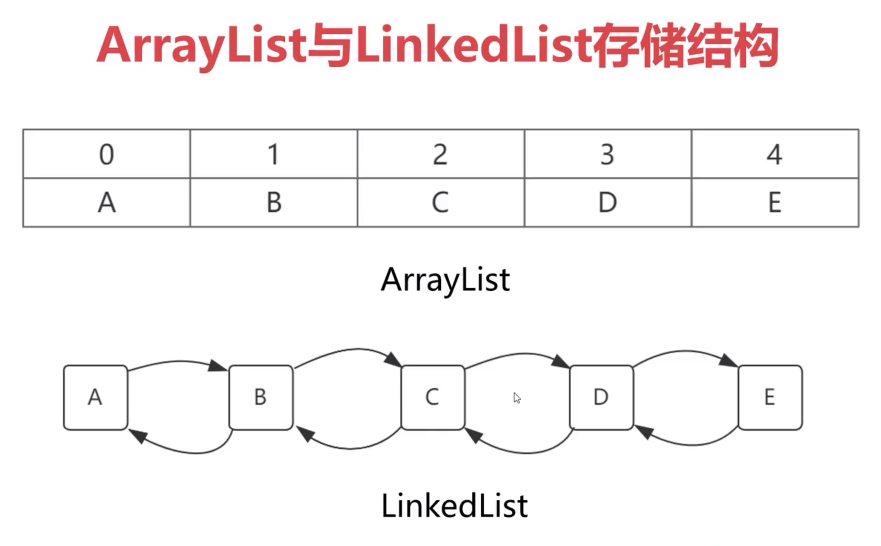
ArrayList(底层是数组/顺序表):
基于数组实现,数据位置有序,自动对容量进行扩容,多数情况下无需指定Max长度,内存中连续紧密存储,数据访问速度快。
注:适合数据变化不大,快速读取场景。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// 创建ArrayList
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
// 添加元素“Test”
arrayList.add("Test");
// 在索引位置1处添加元素“Test2”
arrayList.add(1,"Test2");
// 获取指定位置元素数据(0)
arrayList.get(0);
// 更新索引位置1的元素数据
arrayList.set(1,"XXX");
// 删除索引位置1的元素数据
arrayList.remove(1);
// 删除内容为“XXX”的元素数据
arrayList.remove("XXX");
// 获取List中数据个数/长度
int count = arrayList.size();LinkedList(底层是链表):
同时实现了List和Deque两个接口。有序允许重复,可在队列的队首及队尾快速追加数据。在内存中分散存储,拥有良好的插入速度,数据访问速度低于ArrayList。
注:适合需要频繁修改集合数据场景。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20// 创建LinkedList
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
// 添加元素“Test”
linkedList.add("Test");
// 在索引位置1处添加元素“Test2”
linkedList.add(1,"Test2");
// 获取指定位置元素数据(0)
linkedList.get(0);
// 更新索引位置1的元素数据
linkedList.set(1,"XXX");
// 删除索引位置1的元素数据
linkedList.remove(1);
// 删除内容为“XXX”的元素数据
linkedList.remove("XXX");
// 获取List中数据个数/长度
int count = linkedList.size();
// 在List首部添加元素“Test1”
linkedList.addFirst("Test1");
// 在List尾部添加元素“Test2”
linkedList.addLast("Test2");Vector
Stack
ArrayList与LinkedList存储结构
List集合的三种遍历方式
Collections排序
该方式可以对原始list集合进行内部排序。
1
Collections.sort(list);
自定义排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class ListSorter {
class SampleComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
// 升序 o1-o2 降序o2-o1
public int compare (Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
}
// 调用SampleComparator进行定制排序
public List<Integer> sort(List<Integer> list){
Collections.sort(list, new SampleComparator());
}
}对类进行自定义排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class CustomObjectSortSample {
class CustomComparator implements Comparator<Goods> {
// 升序 o1.getSn().compareTo(o2.getSn())
// 降序 o2.getSn().compareTo(o1.getSn())
public int compare (Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.getSn().compareTo(o2.getSn());
}
}
// 调用SampleComparator进行定制排序
public List<Integer> sort(List<Goods> list){
Collections.sort(list, new CustomComparator());
}
}
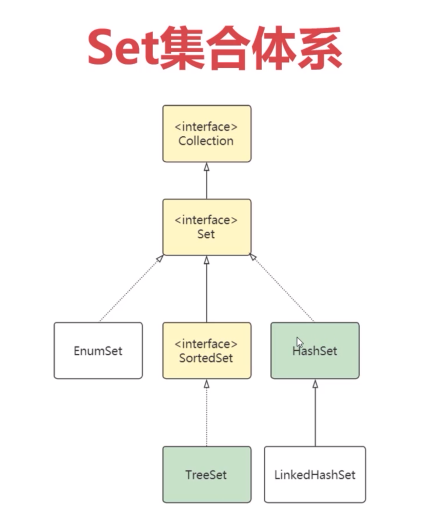
Set:无序,不可重复集合
Set集合体系
HashSet(Set接口的典型实现)
HashSet按Hash算法决定集合元素的顺序,具有很好的查找性能。根据hashCode值决定该对象在HashSet中的存储位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// 数据无序,不可重复,不支持通过索引访问
Set<String> mobileSet = new HashSet<String>();
mobileSet.add("1321323131");
mobileSet.add("1321323132");
// 获取当前Set集合中的数据数量
int count = mobileSet.size();
// 比较Set集合中是否存在相同元素"1321323132"
boolen result = mobileSet.contains("1321323132");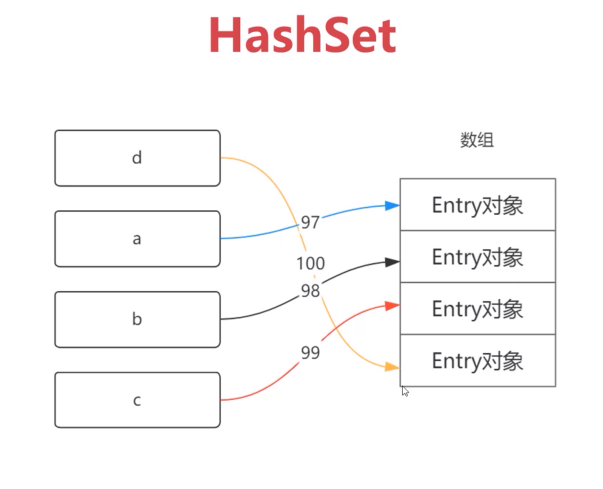
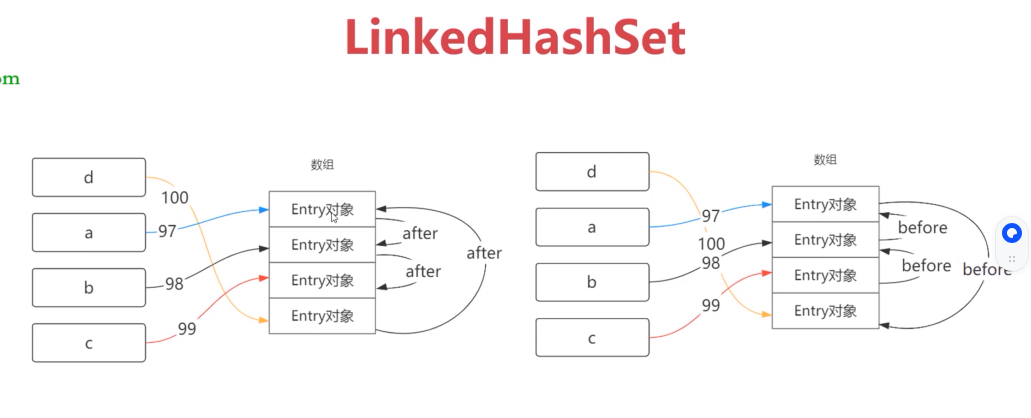
LinkedHashSet(HashSet子类)
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,除HashSet的特性外,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,保障按插入顺序提取数据。
性能略低于HashSet,迭代访问Set中全部元素将有更好的性能。
TreeSet(SortedSet接口的实现类)
TreeSet是SortedSet接口的实现类,可以保证集合元素处于排序状态。采用红黑树的数据结构存储集合元素。默认采用自然排序对元素升序排列,也可以实现Comparable接口自定义排序方式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class TreeSetSample{
class IntegerComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
// 升序 o1-o2 降序o2-o1
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
}
public void sort(){
// 调用IntegerComparator进行定制排序
Set<Integer> s = new TreeSet(new IntegerComparator());
}
}
Set集合如何确保数据唯一性?
Set集合在新增数据时先判断数据的hashCode()是否存在,若hashCode()存在则调用equals()进行值比较;hashCode()与equals()都存在的情况下,Set集合才认为数据已存在,不予新增。
如以一个类中的唯一值作为唯一标识时,需重写这个类中的hashCode()和equals()方法。
为什么用对象的hashCode()而不直接用equals()?
出于执行效率,hashCode()返回的整数结果决定了Set集合中的存放位置,hashCode()计算速度快,但可能出现哈希值碰撞;当出现哈希碰撞时,则使用equals()对值进行比较,处理速度相对较慢。
哈希
Hash,是把任意长度的数据通过散列算法变成固定输出。
Map:映射关系集合(key(键)-value(值))
key和value可以是任何引用类型数据,key通常为String。Map中Key不允许重复,如果重复,则该Key对应的Value值会被覆盖。
Map接口及实现
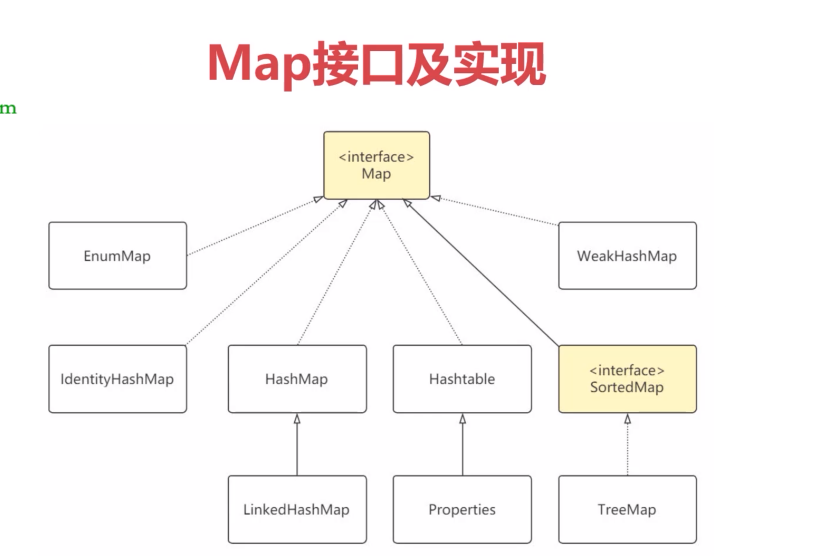
Map体系
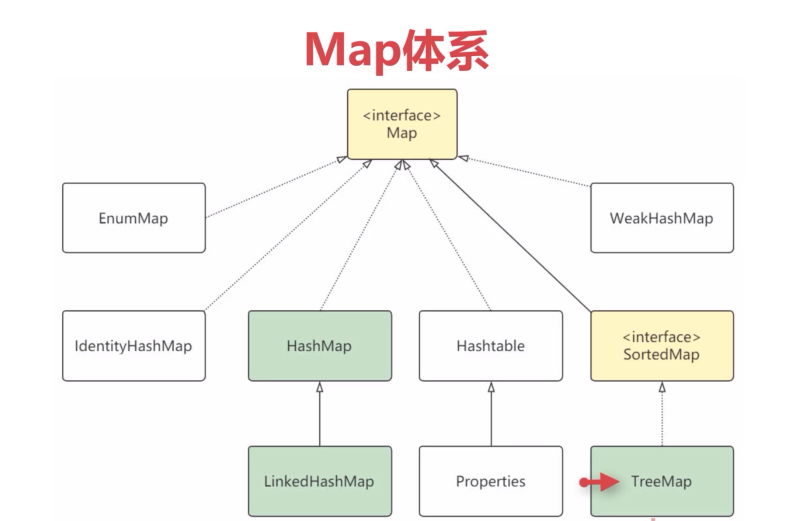
HashMap(Map接口的典型实现类)
对Key进行无序存储,不能保证数据按存储顺序读取,Key全局唯一。
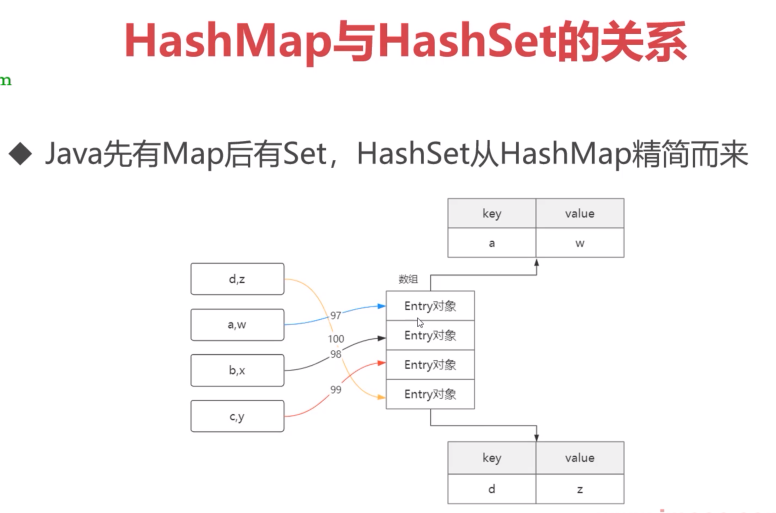
HashMap与HashSet的关系
使用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15HashMap<String, Object> student = new HashMap();
student.put("name","张三");
student.put("weight",60);
// 相同key会覆盖->张三被李四覆盖
student.put("name","李四");
// 获取Map中键值对总数
student.size();
// 获取对应key的value值
String name = (String)student.get("name");
// 判断是否有对应的key
boolean r1 = student.containsKey("name");
// 判断是否有对应的value
boolean r2 = student.containsValue("李四");
// 删除某个键值对,已整型包装类返回该key的value值
Integer w = (Integer)student.remove("weight");
LinkedHashMap
在HashMap基础上增加了链表,保证提取数据时的顺序和存入时的数据相同。
1
2
3LinkedHashMap<String, Object> student = new LinkedHashMap();
// 常用new Map的方式
Map<String, Object> student = new LinkedHashMap<>();TreeMap
TreeMap存储key-value键值对时,需根据key对节点进行排序。
支持自然排序和定制排序两种排序方式。
与TreeSet相同,TreeMap也是基于红黑树结构对数据进行排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20// 自动进行排序
Map<String, Object> record = new TreeMap<>();
record.put("A1","1");
record.put("C1","1");
// 手动进行排序(定制排序)
public class TreeMapSample{
class RecordComparator implements Comparator<String> {
// 字典顺序升序排序(o1.compareTo(o2))
// 字典顺序降序排序(o2.compareTo(o1))
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
}
public void sort(){
// 调用RecordComparator进行定制排序
Map<String, Object> record = new TreeMap<>(new RecordComparator());
}
}Map的三种遍历方式
标准for循环
1
2
3
4
5// 先获取到key,再用key找value
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
for (String key : keys){
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}forEach方法
1
2
3
4// 基于Lambda表达式实现
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + value);
});Iterator迭代器
1
2
3
4
5Iterator<Map.Entry<String Object>> itr = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = itr.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue());
}
Queue:队列特性
Collection接口及实现