Java IO流
IO流
File类
- File类是java.io包下代表与平台无关的文件和目录。
- 程序中操作文件和目录,都可通过File类完成,File类能新建、删除、重命名文件和目录。
- File类本身不能访问文件内容本身,需要利用IO流(输入流/输出流)访问呢。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23// 文件基本操作方法
File f = new File("文件路径");
// 创建文件
boolean r1 = f.createNewFile();
// 删除文件
boolean d1 = f.delete();
// 获取文件路径
f.getPath();
// 判断文件是否存在
f.exists();
// 判断文件是否为目录
f.isDirectory();
// 判断文件是否为文件
f.isFile();
// 获取文件大小
f.length();
// 获取文件名
f.getName();
// 目录基本操作方法
File d = new File("目录路径");
// 创建目录
boolean r2 = d.mkdirs();字节/字符流
流-Stream概念:Java把传输的数据抽象成流的概念,简化程序处理。
Java的IO通过java.io包下类和接口支持。
按出入方向:输入、输出
按内容类型:字节流、字符流
二进制文件(如图片)通常使用字节流进行处理。字符(如文本信息)则使用字符流进行处理。
字节输入流(InputStream)
- InputStream是所有字节输入流的父类
- InputStream提供核心方法read(),用于读取字节数据
- FileInputStream类专用于读取二进制文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25File source = new File("D:\\Java\\Test.txt");
InputStream fis = null;
{
try {
// 对象实例化
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
// 读取目标文件,每次只读1KB
while ((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭IO流
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}字节输出流(OutputStream)
- OutputStream是所有字节输出流的父类
- OutputStream提供核心方法write(),用于向指定输出流输出字节数组
- FileOutputStream类专用于写入二进制文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37File source = new File("D:\\Java\\Test.txt");
File target = new File("D:\\Java\\Test1.txt");
InputStream fis = null;
OutputStream fos = null;
{
try {
// 对象实例化
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
fos = new FileOutputStream(target);
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len;
// 读取目标文件,每次只读1KB
while ((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1){
System.out.println(len);
fos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭输出流
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 关闭输入流
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}字符输入流(Reader)
Reader是所有字符输入流的抽象父类
FileReader对应文本文件的读取
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21File file = new File("D:\\Java\\Test.txt");
Reader reader = null;
int ch = 0;
try {
reader = new FileReader(file);
while ((ch = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出流(Writer)
Writer是所有字符输出流的抽象父类
FileWriter对应文本文件的写入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23File file = new File("D:\\Java\\Test.txt");
Writer writer = null;
try {
// 判断该文件是否存在,不存在则创建
if (!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
writer = new FileWriter(file);
// 该写入会覆盖文件原始内容
writer.write("123456789");
// 该追加方法会在文件末尾追加内容
writer.append("大大");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字节流与字符流之间的转换
字节流转换成字符流:
- InputStreamReader将字节输入流转换成字符输入流
- OutputStreamWriter将字节输出流转换成字符输出流
缓冲区
默认文件的读取与写入都是逐个字节/字符完成的,但这种处理方式并不高效,如果将读取或写入的数据整块在内存中缓存,一次性批量读取、写入,便可以有效提高数据交互效率。
BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream用于缓冲字节输入、输出流。
BufferedReader与BufferedWriter用于缓冲字符输入、输出流。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28File file = new File("文件路径");
FileReader reader = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
String line = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(file);
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (bufferedReader != null) {
try {
bufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}其他常用IO流
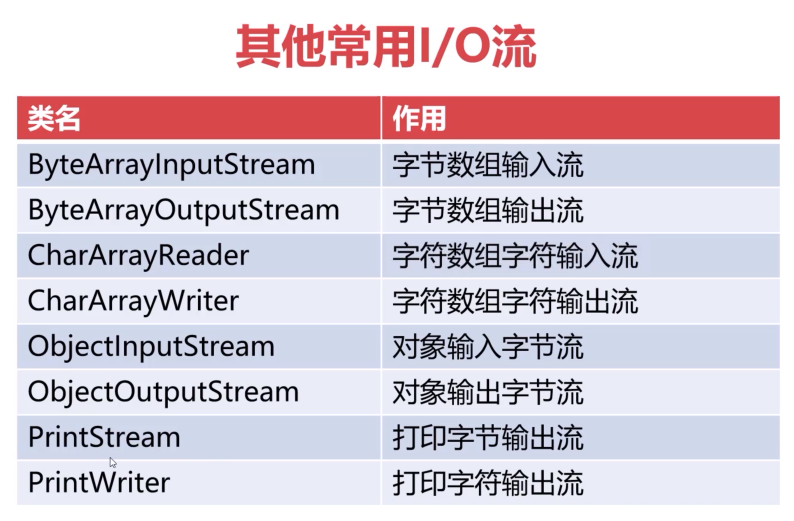
通过URLConnection获取网络资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 网络资源路径
URL url = new URL("https://pic1.zhimg.com/v2-5ca37f685c30dbecc38b8cd88b43918c_r.jpg");
// 建立Connection连接
URLConnection urlConnection = url.openConnection();
// 获取字节输入流
is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
File file = new File("D:\\Java\\Test.png");
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
// 判断该文件是否存在,不存在创建
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
os = new FileOutputStream(file);
int len;
// 开始循环写入二进制数据
while ((len = is.read(bs)) != -1) {
os.write(bs ,0, len);
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 关闭字节输出流
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 关闭字节输入流
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 CodeWhale-Blog!
评论





